Physics 101: Beginner to Intermediate Concepts
Unlock the Mysteries of the Universe: Your Journey from Basics to Brilliance

24 Hours average completion time
2.4 CEUs
15 Lessons
33 Exams & Assignments
11 Discussions
15 Videos
16 Reference Files
94 Articles
Mobile Friendly
Last Updated October 2025
Physics Unveiled: Bridging Concepts with Comprehensive Mathematical Tools
In the realm of natural sciences, Physics reigns supreme as the cornerstone upon which disciplines like chemistry, geology, and biology find their footing. Often touted as the language of the universe, Physics unravels the mysteries of the cosmos, making sense of the world we inhabit. However, this fascinating subject is intertwined with mathematics, which can sometimes act as a barrier for enthusiasts wanting to explore the depths of Physics.
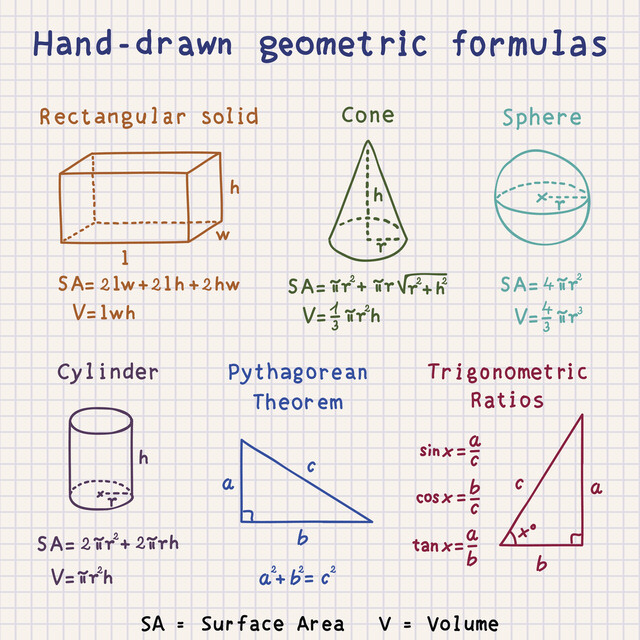
This meticulously curated course is designed to bridge this gap, emphasizing the indispensable mathematical tools that breathe life into the principles of Physics. It's perfectly tailored for those with a foundational understanding of algebra, geometry, and trigonometry. Instead of delving deep into intimidating calculus, we ensure that the mathematical framework presented is both approachable and robust enough for an in-depth exploration of classical Newtonian mechanics and foundational electromagnetism.
Journey Through the Course: Highlights and In-depth Analysis
1. Introduction and Mathematical Foundations: Kickstart the journey by getting acquainted with the mathematical pillars of Physics. Delve into the world of vectors, understanding their significance in representing quantities with both magnitude and direction. For instance, consider the flight of a bird; the speed of its flight and the direction in which it's flying can be represented succinctly using vectors.
2-3. Force and Newton's Laws: Newton's Laws are at the heart of classical mechanics. Explore the intrinsic relationship between force and motion, understanding phenomena from the simple push of a door to the thrust of a rocket propelling into space.
4. Uniform Circular Motion: Have you ever wondered why the planets revolve around the sun in elliptical orbits? Dive into the intriguing world of objects moving in circles and understand the forces acting upon them.
5. Momentum: Picture a game of pool. The way balls move and interact upon collision is governed by the principles of momentum. Grasp the intricacies of this crucial concept.
6-7. Work and Energy: Energy is a concept that is pivotal to understanding various physical phenomena. From the energy stored in a stretched rubber band to the work done by a crane in lifting heavy objects, unravel the concepts of work, kinetic energy, and their interrelationships.
8. Mechanical Energy and Power: Delve deeper into the world of energy, understanding its forms and the rate at which work is done, which is power. Consider the power generated by massive dams or the mechanical energy stored in a coiled spring.
9. Electrostatics: Remember the little spark when you sometimes touch an object? That's electrostatics in play! Uncover the mysteries of electric charges, their interactions, and the forces they exert.
10. Currents and Magnetism: Explore the mesmerizing realm of electric currents and magnetism. From the simple compass pointing north to the massive generators producing electricity, understand the synergy between electricity and magnetism.
11-13. Waves: Waves are everywhere! From the ripples in a pond to the radio waves carrying music to our radios. Dive into acoustic waves produced by musical instruments and the electromagnetic waves that power our modern communication devices.
14-15. Rays and Geometrical Optics: Step into the world of light. How do lenses work? How can mirrors form images? Answer these questions and more as you navigate the fundamental principles of optics.
Empowerment Through Knowledge
By the culmination of this course, students will possess a treasure trove of mathematical tools and conceptual knowledge, empowering them to delve deeper into the vast universe of Physics. Whether you aim to pursue advanced studies, embark on a career in scientific research, or simply satiate your curiosity about the world around you, this course acts as your compass, guiding you through the captivating terrains of Physics.
So, are you ready to unravel the mysteries of the universe, one equation at a time? Join us on this enlightening journey, where every lesson unveils a new layer of understanding, bringing the cosmos a step closer!
- Investigating electrostatic forces and interactions
- Calculating work and energy efficiently
- Grasping momentum and conservation principles
- Examining electric currents and magnetic fields
- Applying Newton's laws to real-world scenarios
- Analyzing forces and predicting motion
- Interpreting wave behavior and properties
- Comprehending mechanical energy and power
- Exploring circular motion mechanics
- Navigating geometrical optics principles and applications
- Understanding mathematical foundations of physics
Choose from plans starting at just $16/month (billed annually)
See Your Team Succeed
Empower your team instantly with an integrative group enrollment system. Purchase licenses in bulk with Group Discounts.