Key Definitions
1. Pension Plan - a plan for keeping money for retirement use.
2. IRA (Individual retirement account) � a personal retirement account with a financial institution such as a bank or mutual fund company.
3. Social security - any governmental system providing monetary aid to people with no or insufficient income.
4. Defined contribution pension - retirement savings built from both employee's and employer's contributions (when applicable).
5. Year of Service � your employment working period covered by a plan. Usually used to determine when you participate and gains rights and how you can increase benefits in the defined contribution plan.
6. 401-K plan - is a defined contribution plan, funded by employee's contribution and matched by employer's contribution. There are two types pre-tax contributions( traditional 401-k) and post-tax contributions( Roth 401-k)
7. Reinvestment � transfer of saving funds from one account to another by an employee upon changing jobs. Usually, transfer is to a new plan or IRA.
Starting to save early for retirement is one of the best ways to become debt-free and gain financial freedom and security. Saving for retirement removes tomorrow doubts by allowing you to set money aside for retirement years. In this article, we will examine the importance of saving for retirement early.
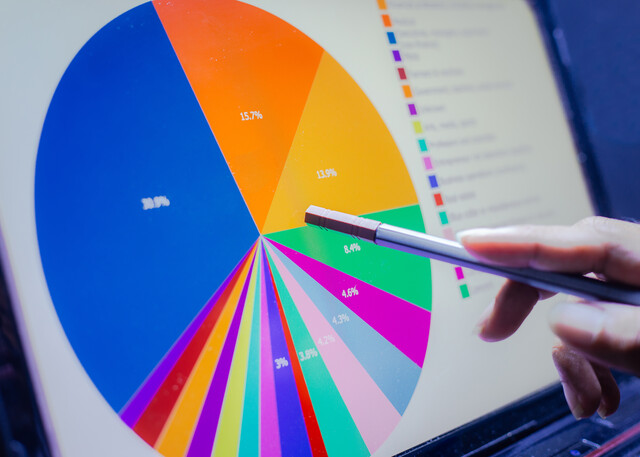
One of the best decisions a young person can make is to starting contribute as much as he or she can to a retirement scheme like a 401(k). Contributing over a long time increases the overall amount of money you contribute, the interest earned as well as the compounding effect on your savings. The graphs below show the effect on your retirement income if you postpone your contributions to a 401(k) or other retirement schemes.
The chart is based on these assumptions:
-
Your annual income is $42,000 at age 30
-
Your annual income increases by 3 percent each year.
-
Your annual contribution rate is 7% of your annual income.
-
Your employer match is 3 percent of your annual income
-
Your annualized investment rate is 7%.
As shown in the graphs, during the early years, for every year that your delay your decision to save, your potential annual lifetime withdrawal income decreases by 2 to 3 percent � this holds true during the early years. However, in late years, the effect of the missed years of compounding returns becomes alarmingly huge - the early savers are advantaged.
For example, if you begin saving 10 percent of your income at age 35, you would realize an annual lifetime income of $19,999 compared to $22,467 if you started to save at age 30.
Next, let's burst the common myth about saving for retirement.
1. I will continue to work even after retirement."
-
67% of corporate Americans say they plan to work well beyond retirement � but only 22 percent of the current retirees end up doing it.
-
A number of factors that can make one to retire early. See the diagram below:
|
You may not have full control over your retirement age, so start saving early and create your safety net.
2. "I will claim my Social Security benefits early."
-
Claiming your benefits early reduces the amount you receive. In fact, given that life expectancy is increasing, it might be wise to delay claiming your benefits.
3. "My spending habits will not change significantly after retirement."
-
The impact of inflation is felt more by retirees. They are the age group that consumes most of the goods whose prices are heavily impacted by inflation such as healthcare.
4. "Retirement is still far away � I have enough time to plan for it."
-
The sooner you begin to save, the more you start to gain from the power of compound interest. Debts, missed contributions, and early withdrawals result in less saving, low compounding and few assets upon retirement.
|
Starting to save for retirement early gives optimal benefits mainly due to the massive power of compounding over a long-time.
5. "I have already saved a little � I am fine."
-
Sad enough, in 2015, only 48 percent of working Americans and/or couples had computed how much they should save to enjoy comfortable retirement. Utilize the saving checkpoint given below to see whether you are on the right track.
6. "I have already reached my saving target. I will be fine after retirement given the decreasing cost of living."
-
Expenditure doesn't decrease during the first years after retirement. True, some expenses decline with age, but most remain constant or increase. See the diagram below that shows changes on expenditure as one ages:
|
Note: Expenditure reaches peak at the age of 45, and then it starts to decrease except for charitable donation, gifts and healthcare. Housing remains the largest expense even during old age.
7. "The market is currently too unstable; I will wait so that I don't lose."
-
Do not shy away from investing during volatile economy. You stand to win from market rallies.
-
Set SMART retirement goals upfront - and focus on the long-term even during times of uncertainty and volatility.
The diagram below will give you some ideas on how to structure your investment during times of unstable markets.
Diagram notes:
-
Bonds are affected by interest rate risk. Their prices fall when interest rate increases.
-
The price of shares rises or falls with changes in the wide market factors or the specific company financial standing, sometime gradually, unpredictably and/or rapidly. Stock market securities are subject to stock market risks.
-
Alternative investments are only suitable in the long run primarily because they feature higher risks than traditional investments.
-
Fixed cash and income and equity are classified under traditional asset.
-
As used in the diagram above, the word "alternative" refers to all non-traditional asset categories. These include venture capital, venture capital, public equity, hedge funds, commodities, distressed debt and more.
A sound retirement plan makes the most of the factors you can control while managing the factors you have little or no control over. See the diagram below;
Source: Employee Benefit Research Institute, 2015 Retirement Confidence Survey.
Importance of Starting To Save Early for Retirement
Retiring at an early age with a fat bank account
Basically, the earlier you start saving for retirement, the higher the compound interest you stand to earn. For example, a fresh college graduate who saves $200 on a monthly basis until age 65 and earning 5% interest on his annual pension contributions is likely to accumulate up to $550,000. On the contrary, a mid-forty individual contributing the exact amount each month and earning 5% interest is likely to accumulate only $138,000 by age 65. Other benefits of retiring early include:
Time to explore the world: With your new found freedom and financial stability that result from starting to save early for retirement, you will be free to explore the world as much as you want. Your health will be in perfect condition allowing you to enjoy some activities that can't be performed by those who retire at a later age.
Enough time with loved ones: Have you always been away from your kids? Retiring early gives you the opportunity to enjoy time with your loved ones and to age gracefully. You will not only have time to see the birth of your grandchildren but also time to spoil them with love.
Freedom to start a new career: With the yester years all washed away, most individuals crave for a career change. The boredom of working on your occupation for decades calls for a fresh start. What better timing than when you have retired! Retiring early gives you time to start the journey of a new life career - think motivational speaking or politics for the charismatic few.
Avoiding procrastination: If you do not begin saving for your retirement today, when will you? I know tomorrow sounds great, but you don't know what it will bring. According to a survey done by MoneyRates.com, a consumer saving website, only 52 percent of people begin to save for retirement by age 40, and savings rates often drop until they near their retirement age.
Finding compatible social friends early: The earlier you start to save, the more likely that you will end up chilling out with saving-minded people. This helps you to enjoy your life while using less money - you do a lot of activities with your like-minded friends.
Additionally, when you begin to search for a future wife/husband, you will most likely get a person who shares your objectives of retiring early with a comfy nest egg.
You become more confident: Never underestimate the power you possess when you realize that you have the assets to survive any storm. By starting to save early for retirement, you always know that you will be okay no matter what happens later in your career. You even become less afraid of becoming unemployed, and that confidence may be exactly what you need to move on to higher positions in your firm.